Five Ways Artificial Intelligence in FinTech is Changing the Industry

AI in the financial technology market
Artificial intelligence has become a promising technology for enterprises from various sectors of the economy. Financial companies are pioneers and leaders in this field. Autonomous Research calculated that by 2030 AI will save the industry up to 22% of the funds. Forrester estimates that about half of the world’s banks and insurance agencies are using smart algorithms in their transactions, and the demand for FinTech development services continues to grow. Let’s consider the value of artificial intelligence in FinTech.
AI statistics in the financial sector in 2022
When financial companies implement AI, their main goal is to reduce transaction costs. Among other significant benefits are improved data management and increased employee productivity.
In 2021, most financial institutions partially implemented smart algorithms in their transactions. Only a third of Statista’s survey participants say they have fully embraced the technology.
By 2026, the share of artificial intelligence in FinTech will almost triple. It will reach $26.67 billion. Organizations are interested in this innovation and invest in AI-powered projects to automate operations and expand businesses.
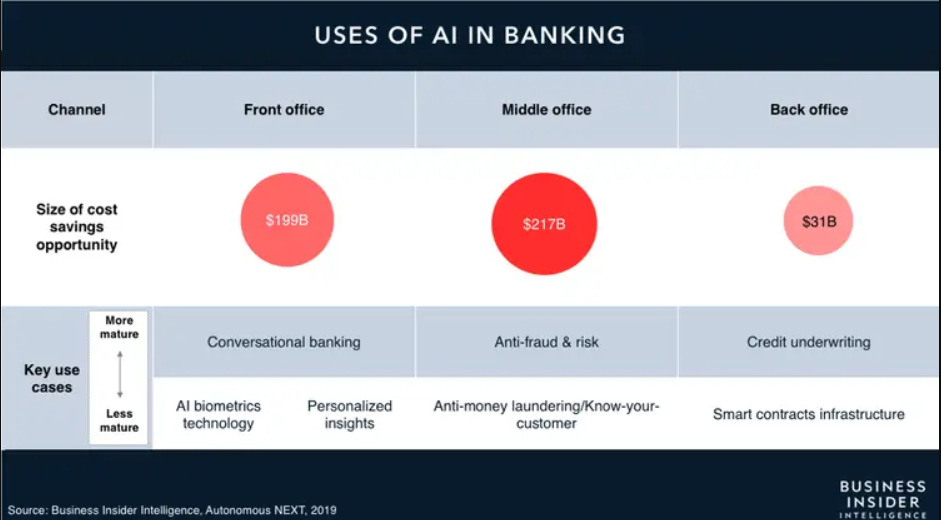
The value of AI for financial companies
Artificial intelligence in finance supports many traditional procedures, from front to back offices.
Artificial intelligence is used in many sectors:
- banking;
- insurance services;
- loans/credits;
- personal finance;
- digital payments;
- venture capital;
- wealth management.
FinTech companies benefit from AI. The technology helps to work with data, which is a rich competitive resource. Businesses use only 0.5% out of 44 zettabytes of data generated annually. There is a lot of information in the financial industry: browser specifications, transaction history, images, confidential information, etc.
A smart algorithm optimizes work with data to get the maximum benefit for your business. It will help you to:
1. Accurately access credit risks
Lending is the largest niche in the financial industry. In 2020, America alone had approximately $4.17 trillion in outstanding consumer credit, which is $62.4 billion more than a year earlier. Negligent payers are becoming a problem for banks.
Banks scrupulously check candidates for solvency to prevent a financial catastrophe. It is difficult to perform this task manually: bank employees need to analyze the credit rating, familiarize themselves with loan applications, calculate payments, and approve or reject the client’s request.
Artificial intelligence automates underwriting. A smart algorithm analyzes the candidate’s digital footprint: social media profile, web resource browsing history, geolocation. The technology evaluates the collected information and provides bank employees with conclusions about credit risks.
AI-based underwriting pays off. Thanks to this technology, companies increase the percentage of loan approvals and extend the periods of payments. They trust borrowers, offer more money for longer terms without risks to their businesses.
2. Save resources.
By adopting AI-powered applications, banks will save $447 billion by 2023. Emerging Technologies calculated that smart algorithm adherents increase their annual revenue by 58%.
To increase profits, banks do not need to raise the price. They offer better deals for customers through improved processes. Users do not turn to competitors because it is convenient for them to work with the bank. The conversion is growing, and so is the income.
Savings become possible through AI automation. Previously, procedures were performed manually and took more time. Artificial intelligence takes over such responsibilities as data analysis, underwriting, and approval of applications. Employees complete more tasks over the same period.
3. Personalize services.
In pre-technological times, bankers needed to know customers personally to help them manage their money rationally. Today, when every bank has a ten-hundred-million clientele, and most transactions occur through banking applications, it is more difficult to “please” individual consumers. More than 50% of financial services users believe that personalization makes them trust their banks. Only 35% of financial institutions can respond to these demands.
Artificial intelligence allows organizations to analyze a large amount of consumer information quickly. Based on the results, the algorithm selects relevant products that meet individual demands. As a result, users get what they like and continue to cooperate with the financial company. Increasing customer retention by just 5% increases profits by 25%.
4. Detect fraudsters.
The industry has always had concerns about protecting customer privacy. The pandemic has forced financial institutions to adapt their business models to the new rules. For example, they have switched to remote lending. Consumers are more likely to pay for products online, use digital wallets, and use P2P payments. As a result, there have appeared additional loopholes for attackers.
PwC found that in 2020, a business was attacked six times on average, which cost $42 billion. FinTech data breach costs are among the highest at $5.72 million.
A smart algorithm monitors the behavior of users of a banking or insurance application, automatically detects fraud threats, and reports suspicious activities. For example, if a borrower tries to apply for ten identical loans in 5 minutes, artificial intelligence detects this behavior as an anomaly and alerts cybersecurity specialists.
5. Make accurate predictions.
Good analytics in FinTech affects sales growth, business development, and competitiveness. It may depend on predictions whether a loan will be issued to a reliable person or an insolvent one; what financial products will be useful to customers in the future, and so on. To find a pattern in processes and draw reasonable conclusions, it is necessary to study a huge amount of data, learn how to store and protect it. It is rather difficult to do this manually. Smart tools are needed to transform data into valuable information. One of them is AI.
Artificial intelligence examines stored customer data and “tells” managers how to use the information profitably. A person can predict demand based on the sales data from previous years without using machines. But only artificial intelligence can reveal complex and unexpected variables.
How to implement artificial intelligence in FinTech
While many financial institution owners see AI as experimental or utopian, pioneers in adopting the technology are already getting practical results. Therefore, it is worth developing certain business processes to pave the way for artificial intelligence.
Deloitte has identified six steps to harness the power of AI:
- To develop an AI strategy.
It is necessary to establish which processes the company wants to improve with the help of AI, whether it plans to use the technology partially or everywhere. It should familiarize itself with the technology, add it to the culture of the organization and adapt AI to the business goals of the enterprise. The employees should decide what needs to be done and how to make the technology useful.
2. To define use cases for AI.
This is the most difficult step in introducing AI into an organization. Some companies are rushing to adopt the technology just because it is popular. They don’t realize its value and long-term perspectives. A smart algorithm gives a lot of opportunities that we have mentioned above. It is worth choosing priority use cases and evaluating their benefits and possible drawbacks. So, the company will understand how to start AI software development.
3. To create a prototype.
To determine whether it is technically possible to implement an AI use case in an organization, whether it is worth investing money in a solution, it is necessary to create a prototype. It is important to check how this solution will function alongside the existing ones. Make sure your employees are ready for a dramatic change in their work. Estimate whether the investment in the AI application will pay off.
4. To consider privacy.
Typically, technology testing, risk assessment, legal and ethical issues take place in the last stages of AI software development. They should be discussed before the start of the project. Thus, you will build an application taking into account the requirements of privacy and legislation.
5. To create a reliable team.
To make the idea of adopting AI a reality, you should assign a team that will help to introduce the technology into a business process. You will need a data specialist, a UX designer, developers, a tester, and other employees to work on the project. When a company does not have such personnel, it is not practical to hire temporary employees. Consider outsourcing IT services.
6. To maintain the technology after the deployment.
AI support and training continue after the implementation of the software. It is necessary to analyze how AI models react to various input data and improve the algorithm. If you ignore this step, the model will drift and start to produce inaccurate results.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence in FinTech creates a better financial environment for banks and their clients. You need to be mentally and technically prepared for the change to implement the technology. It is worth enlisting the support of a FinTech development company that will create an AI application, deploy the software in your organization, and upgrade the product when necessary.